The transformation of raw materials into final commodities involves a number of manufacturing processes. The majority of these procedures involve providing the basic materials a new shape and form by altering either their state or shape. One such crucial procedure is grinding, which is a very effective method for quickly removing metal and for the superior finishing of finished products.
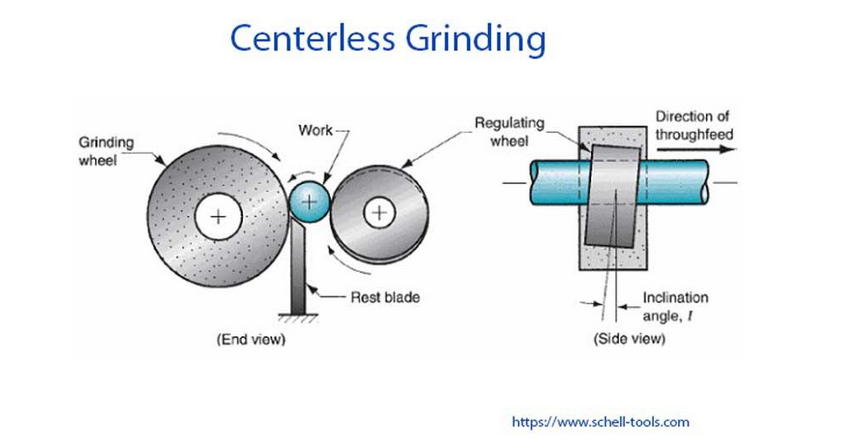
Abrasive cutting is used in the centerless grinding process to remove material from a workpiece. The difference between centerless grinding and centred grinding operations is that the workpiece is secured between two rotary grinding wheels, and the rate at which material is removed from the workpiece depends on how quickly the wheels rotate relative to one another. No spindle or fixture is used in centerless grinding to locate and secure the workpiece.
In order to meet the ever-increasing demands of traditional and specialised industries, such as those producing watches, ball and roller bearings, automobiles, and space rockets, among others, centreless grinding is one of the production techniques used globally for finishing a wide range of components.
Since the need for precision components has grown over the past few decades, significant progress has been achieved in the development of efficient methods for achieving dimensional accuracy and fine surface quality. Although the fundamentals of centerless grinding have been understood since the turn of the 20th century, the first machine was commercially available in 1921. However, it quickly proved to be very helpful in a variety of industries, including ball and roller bearings, the automotive industry, and aviation.
One of the fastest and most cost-effective devices for grinding cylindrical work with diameters close to zero to 600mm and lengths ranging from 1mm to 15mm is a modern centerless grinding machine using the most recent technology.
When several pieces need to be handled quickly, centerless grinding is frequently chosen over other grinding techniques.
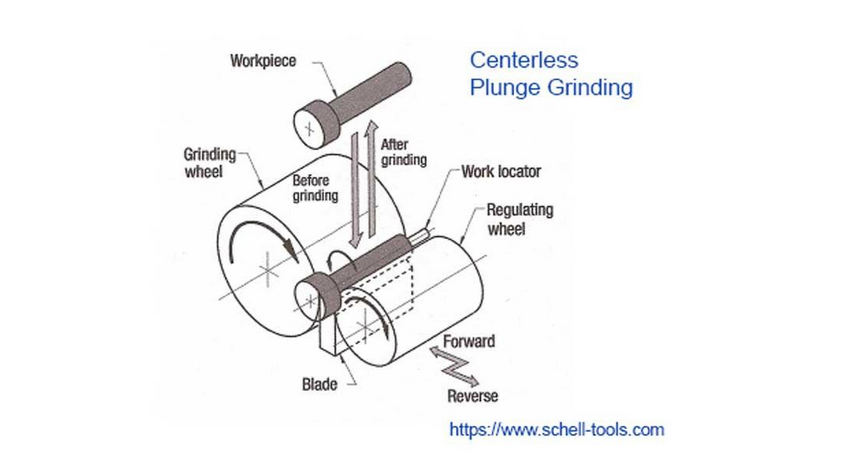
The major pillar of support for the job work is the work rest blade. The blade is one of the most crucial parts of this procedure because it supports the work and determines where the work centre is in relation to the line connecting the grinding wheel’s centre and the regulating wheel’s centre.